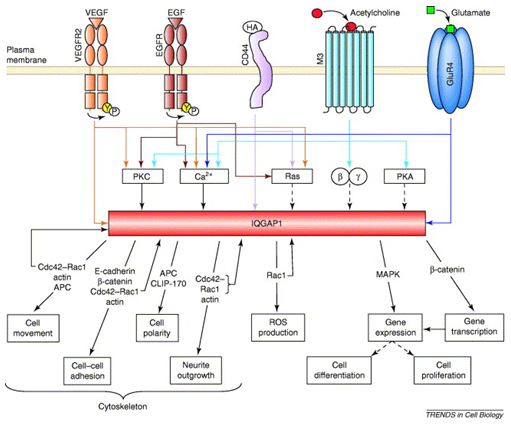
IQGAP1 participates in diverse signaling pathways. In part, this is accomplished via interactions between IQGAP1 and a variety of receptors, including receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and chemokine receptors. IQGAP1 modulates signaling from receptors in multiple ways. For example, IQGAP1 directly regulates activation of some RTKs (e.g. EGFR, HER2, PDGFR). IQGAP1 also regulates the cytoskeleton downstream of receptors. Additionally, IQGAP1 scaffolds downstream signaling components, such as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt pathways. The role of IQGAP1 as a scaffold in the MAPK pathway has been well characterized. Activated RTKs initiate phosphorylation cascades that are critical for the MAPK pathway. IQGAP1 scaffolds MAPK signaling components, including Ras, RAF, MEK and ERK. These interactions promote ERK activation, which then phosphorylates substrates in the cytoplasm and nucleus to facilitate cellular processes. IQGAP1 interactions with diverse signaling molecules facilitate cellular responses to a variety of stimuli, to mediate processes like migration, adhesion and cellular proliferation.